4.4.1 Sound Wave 1
Quiz Summary
0 of 16 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
0 of 16 Questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 16
1. Question
1 point(s)Why can ultrasound not be heard by humans?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 2 of 16
2. Question
1 point(s)A sound wave has a certain amplitude and a certain frequency.
A second sound wave is quieter and lower in pitch than the first sound wave.
The second wave has
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 3 of 16
3. Question
1 point(s)What is the approximate range of hearing of a healthy human ear?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 4 of 16
4. Question
1 point(s)A singer sings two notes. The first note is louder and lower in pitch than the second note.
Which statement about the two notes is correct?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 5 of 16
5. Question
1 point(s)Which range of wave frequencies includes only sounds that can be heard by a human with normal hearing?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 6 of 16
6. Question
1 point(s)A candle flame is placed in front of a loudspeaker.
The loudspeaker produces a sound wave that causes air particles to vibrate. The vibrating air particles make the candle flame vibrate in the same direction as the air particles.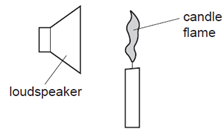
Which row shows the direction of vibration of the candle flame, and the nature of sound waves?
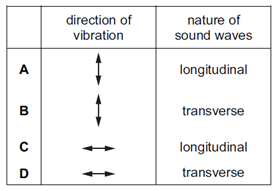 CorrectIncorrect
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 7 of 16
7. Question
1 point(s)A sound wave travels from a point \(X\) to another point \(Y\).

Which diagram represents the movement of the air molecules, due to the sound wave, in the region between \(X\) and \(Y\) ?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 8 of 16
8. Question
1 point(s)Sound wave \(\mathrm{P}\) has a greater amplitude and a larger wavelength in air than sound wave \(\mathrm{Q}\).
How do the loudness and pitch of \(P\) compare with the loudness and pitch of \(Q\) ?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 9 of 16
9. Question
1 point(s)An echo-sounder on a ship produces a pulse of sound. The echo is received by the echo-sounder after two seconds.
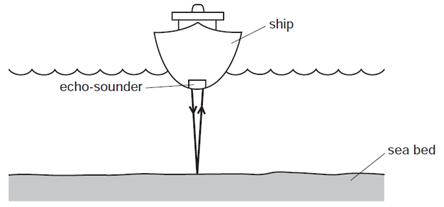
The speed of sound in sea-water is \(1500 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\).
What is the depth of the sea-water below the ship?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 10 of 16
10. Question
1 point(s)Which frequency produces a sound that can be heard by a person?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 11 of 16
11. Question
1 point(s)A scientist tries to direct a ray of light in a glass block so that no light escapes from the top of the block.
However, some light does escape.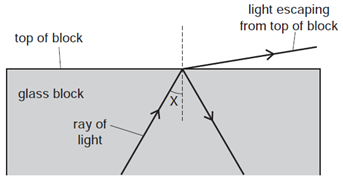
The scientist changes angle \(X\) and stops the light escaping from the top.
Which row in the table describes the change to angle \(X\) and the name of the effect produced?\[
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { change to angle } X & \text { name of effect produced } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { decrease } & \text { total internal reflection } \\
\text { B } & \text { decrease } & \text { total internal refraction } \\
\text { C } & \text { increase } & \text { total internal reflection } \\
\text { D } & \text { increase } & \text { total internal refraction } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]CorrectIncorrect -
Question 12 of 16
12. Question
1 point(s)Which row states two properties of sound waves?
\[
\begin{array}{|c|c|c|}
\hline & \text { can travel through } & \text { type of wave } \\
\hline \text { A } & \text { a vacuum } & \text { longitudinal } \\
\text { B } & \text { a vacuum } & \text { transverse } \\
\text { C } & \text { water } & \text { longitudinal } \\
\text { D } & \text { water } & \text { transverse } \\
\hline
\end{array}
\]CorrectIncorrect -
Question 13 of 16
13. Question
1 point(s)A quiet sound is produced by a loudspeaker. The loudness of the sound is increased. Which property of the sound wave is increased?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 14 of 16
14. Question
1 point(s)A man holding a starting pistol stands \(640 \mathrm{~m}\) away from a spectator.

The spectator hears the sound of the starting pistol \(2.0 \mathrm{~s}\) after seeing the flash from the pistol.
Using this information, what is the speed of sound in air?CorrectIncorrect -
Question 15 of 16
15. Question
1 point(s)A student hearing the sound detects an increase in which property?
CorrectIncorrect -
Question 16 of 16
16. Question
1 point(s)In the experiment shown, the bell is heard ringing. The air is gradually pumped out of the jar. No change is made to the ringing bell.
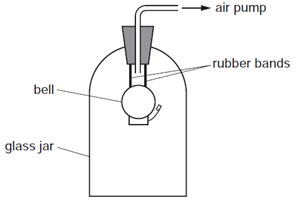
After a few minutes the bell can no longer be heard.
Why is this?CorrectIncorrect