6.3 Strength of Acids and Alkali
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
6.4 Chemical Properties of Acids and Alkalis
5 Topics | 4 Quizzes
6.5 Concentration of Aqueous Solution
6 Topics | 2 Quizzes
6.7 Neutralisation
1 Topic
6.8 Salts, Crystals and Their Uses in Daily Life
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
6.9 Preparation of Salts
5 Topics | 2 Quizzes
6.10 Effect sof Heat on Salts
3 Topics
6.11 Qualitative Analysis
6 Topics | 2 Quizzes
07 Rate of Reaction
7.1 Determining Rate of Reaction
5 Topics | 3 Quizzes
7.2 Factors Affecting Rate of Reactions
7 Topics | 1 Quiz
7.4 Collision Theory
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
08 Manufacture Substances in Industries
8.1 Alloy and Its Importance
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
8.2 Composition of Glass and Its Uses
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
8.4 Composite Materials and Its Importance
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
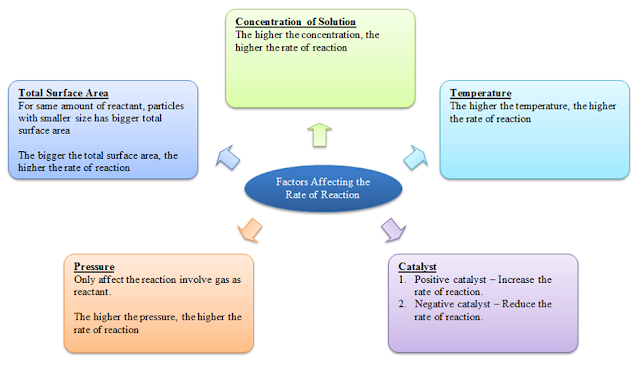
7.2.1 Factors Affecting the Rate of Reaction
There are 4 factors that can affect the rate of a reaction, namely
Negative catalyst – Reduce the rate of reaction.
- the total surface area of the reactant (solid only)
- the concentration of the reactant (solution only)
- the temperature of the reactant
- presense of catalyst in the reactant
- the pressure of the reactant (gas only)
Total Surface Area
- For same amount of reactant, particles with smaller size has bigger total surface area
- The bigger the total surface area, the higher the rate of reaction
Concentration of Solution
The higher the concentration, the higher the rate of reaction.Temperature
The higher the temperature, the higher the rate of reaction.Catalyst
Positive catalyst – Increase the rate of reaction.Negative catalyst – Reduce the rate of reaction.
Pressure
- Only affect the reaction involve gas as reactant.
- The higher the pressure, the higher the rate of reaction