01 Introduction to Chemistry
02 Matter and the Atomic Structure
2.1 Basic Concepts of Matter
7 Topics | 2 Quizzes
2.3 Atomic Structure
5 Topics | 2 Quizzes
2.4 Isotopes and Its Uses
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
03 The Mole Concept, Chemical Formula and Equation
3.1 Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecular Mass
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
3.2 Mole Concept
6 Topics | 4 Quizzes
3.3 Chemical Formula
7 Topics | 1 Quiz
3.4 Chemical Equation
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
04 The Periodic Table of Elements
4.1 Introduction to Periodic Table
5 Topics | 1 Quiz
4.2 Group 18 Elements
2 Topics | 1 Quiz
4.3 Group 1 Elements
6 Topics | 1 Quiz
4.4 Group 17 Elements
7 Topics | 1 Quiz
4.5 Period and Transition Metal
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
05 Chemical Bond
5.1 Basics of Compound Formation
6 Topics | 2 Quizzes
5.2 Ionic Bond
3 Topics | 1 Quiz
5.3 Covalent Bond
4 Topics | 1 Quiz
06 Acids, Bases and Salts
6.2 pH Value
2 Topics
5.6.1 Metallic Bond
- Metal atoms are arranged closely packed and orderly in the solid state. Valence electrons of metal atoms can be donated easily and delocalised.
- When valence electrons are delocalised, metal ions that are positively-charged are formed.
- All delocalised valence electrons move freely between the metallic structure and form a sea of electrons.
- The electrostatic force of attraction between the sea of electrons and the positively charged metal ions form the metallic bond.
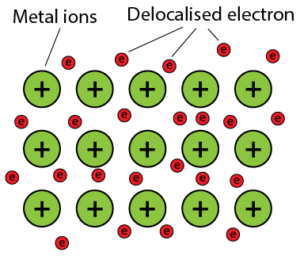
Formation of metallic bond - Metals can conduct electricity due to the free-moving electrons which are delocalised in the sea of electrons.
- The electrons that move freely in the metallic structure carry the charges from the negative terminal to the positive terminal when electricity is supplied.

Electrical conductivity of metals