6.2 Nuclear Energy
5 Topics | 2 Quizzes
07 Quantum Physics
7.1 Quantum Theory of Light
5 Topics
7.2 Photoelectric Effect
2 Topics
7.3 Einstein’s Photoelectric Theory
5 Topics
7.3.1 Einstein’s Photoelectric Theory
- The behaviour of photoelectrons in the photoelectric effect can be explained by Einsteịn’s photoelectric equation:
\[
h f=W+\frac{1}{2} m v_{\max }^2
\]
\(h=\) Planck’s constant
\(f=\) frequency of incident light wave (photon)
\(W=\) work function
\(m=\) mass of photoelectrons
\(v_{\max }=\) maximum velocity of photoelectrons - Assuming that one photon emits one photoelectron, Einstein’s equation is consistent with the principle of conservation of energy:
\[
E = W +K_{\max }
\]
\(E =\) energy of incident photon
\(W =\) work function
\(K_{\max } =\) maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron - In the graph in Diagram below, gradient of the graph = Planck’s constant, \(h\).
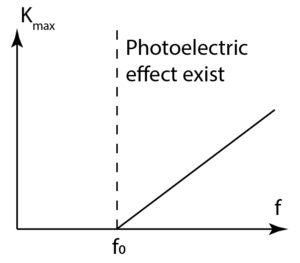
- Thus, the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectron increases linearly with the frequency of the incident photon.