Questions
- Which of the following statements is not true?
- Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass.
- The particle theory of matter states that matter is made up of a large number of tiny and discrete particles.
- The kinetic energy of the particles in a matter increases if its temperature increases.
- The particles in all kind of matter are identical.
- Which of the following shows the correct comparison of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a solid, liquid and gas for a given substance?
- Solid > Liquid > Gas
- Solid < Liquid < Gas
- Solid = Liquid = Gas
- It depends on what kind of substance it is.
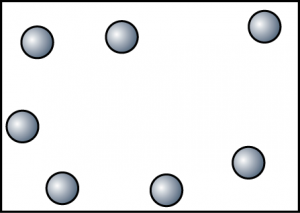
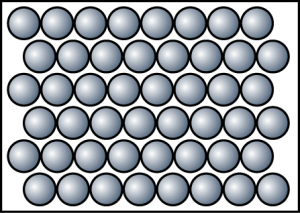
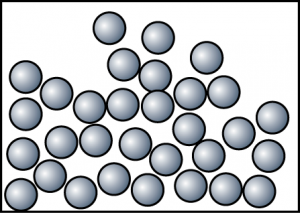
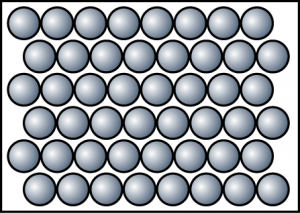
- The diagram shows the arrangement of particles in a substance. Which of the following is not the characteristic of the substance in this state?
- Particles move randomly and slowly and sometimes will collide against each other.
- The volume of the object is not fixed.
- Particles are not arranged in order. Most of the particles are still in contact with one another.
- Difficult to be compressed.
- Which of the following statements is not true about the particles in a gas?
- The particles of gas move at high speed
- The collision between the gas particles and the wall of the container is elastic.
- The gas particles move randomly in all direction.
- The gas particles are arranged in regular patterns.
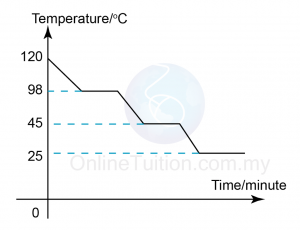
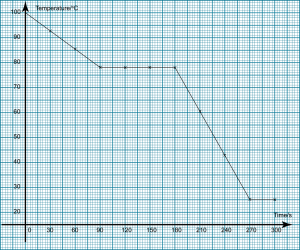
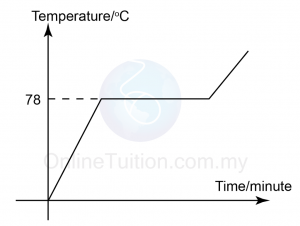
- Which of the following take place when water solidifies to become ice?
- Water molecules get nearer to each other.
- Energy is absorbed from the surrounding.
- Water molecules are not arranged orderly.
- The mass increase.
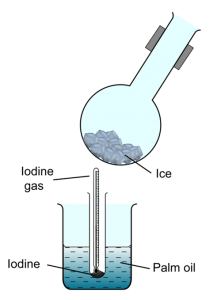
- Which of the following substances sublimes at room pressure when heated?
- Iodine
- Dry ice (Solid carbon dioxide)
- Naphthalene
- Ammonium Chloride
- The particle theory of matter states that
Matter is made up of a large number of tiny and discrete particles.
Which of the following phenomenon does not support this hypothesis?- Brownian Motion
- The shape of a solid is fixed.
- Diffusion of bromine vapour in gas.
- The volume of a substance increase when it transforms from a liquid into gas.
Take the Test
[WpProQuiz 3]