Diffusion in Solid
 |
| Diffusion in Solid |
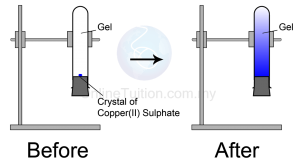
Observation
The blue colour of copper(II) sulphate fills up the entire test tube after a few days
- Copper(II) sulphate crystals are made of copper(II) ions and sulphate ions which are tiny and discrete.
- The particles in the copper(II) sulphate crystal will separate to become ions and diffuse randomly upwards until the whole agar turns blue.