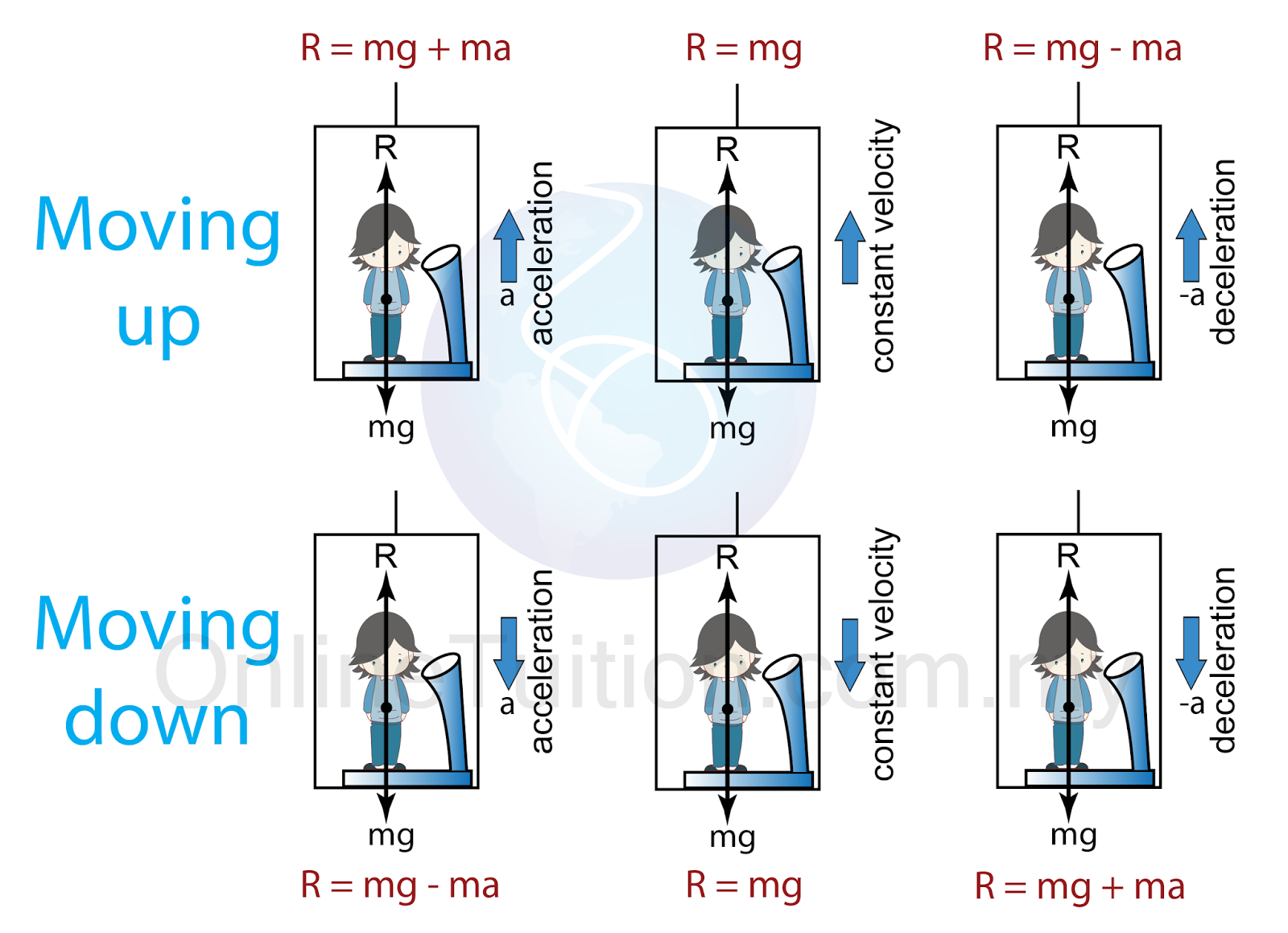
- When a man standing inside an elevator, there are two forces acting on him.
- His weight, (W) which acting downward.
- Normal reaction (R), acting in the opposite direction of weight.
- The reading of the balance is equal to the normal reaction (R).
- Figure below shows the formula to calculate the reading of the balance at different situation.
Example 1:
Subra is standing on a balance inside an elevator. If Subra’s mass is 63kg, find the reading of the balance when the lift,
- stationary
- moving upward with a constant velocity, 15 ms-1.,
- moving upward with a constant acceleration, 1 ms-2.
- moving downward with a constant acceleration, 2 ms-2.
Answer:
a.
W = mg
W = (63)(10) = 630N
b.
W = mg
W = (63)(10) = 630N
c.
R = mg+ma
R = (63)(10)+(63)(1)
R = 693N
R = (63)(10)+(63)(1)
R = 693N
d.
R = mg−ma
R = (63)(10)−(63)(2)
R = 504N
R = (63)(10)−(63)(2)
R = 504N
Example 2:
A 54kg boy is standing in an elevator. Find the force on the boy’s feet when the elevator
- stands still
- moves downward at a constant velocity of 3 m/s
- decelerates downward with at 4.0 m/s2,
- decelerates upward withat 2.0 m/s2.
Answer:
a.
W = mg
W = (54)(10) = 540N
b.
W = mg
W = (54)(10) = 540N
c.
R=mg+ma
R=(54)(10)+(54)(4)
R=756N
R=(54)(10)+(54)(4)
R=756N
d.
R=mg−ma
R=(54)(10)−(54)(2)
R=432N
R=(54)(10)−(54)(2)
R=432N